Economic Dynamics in Eric Ugland’s ‘The Good Guys’ Series
Introduction
This report examines the economic systems and dynamics present in Eric Ugland’s popular LitRPG series, “The Good Guys.” We will explore how the author integrates economic principles into the game-like world, analyzing their impact on character development and plot progression. The report will include a mathematical model of the in-game economy, a visual representation of economic trends, and a comparative analysis of different economic zones within the series.
Main Body
The Mathematical Foundation of the In-Game Economy
In “The Good Guys,” the in-game economy is governed by a complex system of resource generation, currency valuation, and market dynamics. We can model the basic economic growth within the game using a modified version of the Solow-Swan model, as shown in Equation 1:
\[ Y(t) = K(t)^\alpha (A(t)L(t))^{1-\alpha} e^{\beta Q(t)} \tag{1}\]
Where:
- Y(t) is the total production in the game world at time t
- K(t) is the capital stock
- A(t) is the level of technology
- L(t) is the labor force (players and NPCs)
- Q(t) represents the impact of quests and missions
- \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) are constants representing the elasticity of output with respect to capital and quests, respectively
This equation demonstrates how the unique elements of the game world, such as quests (Q), interact with traditional economic factors to drive growth and development.
Economic Trends Across Game Zones
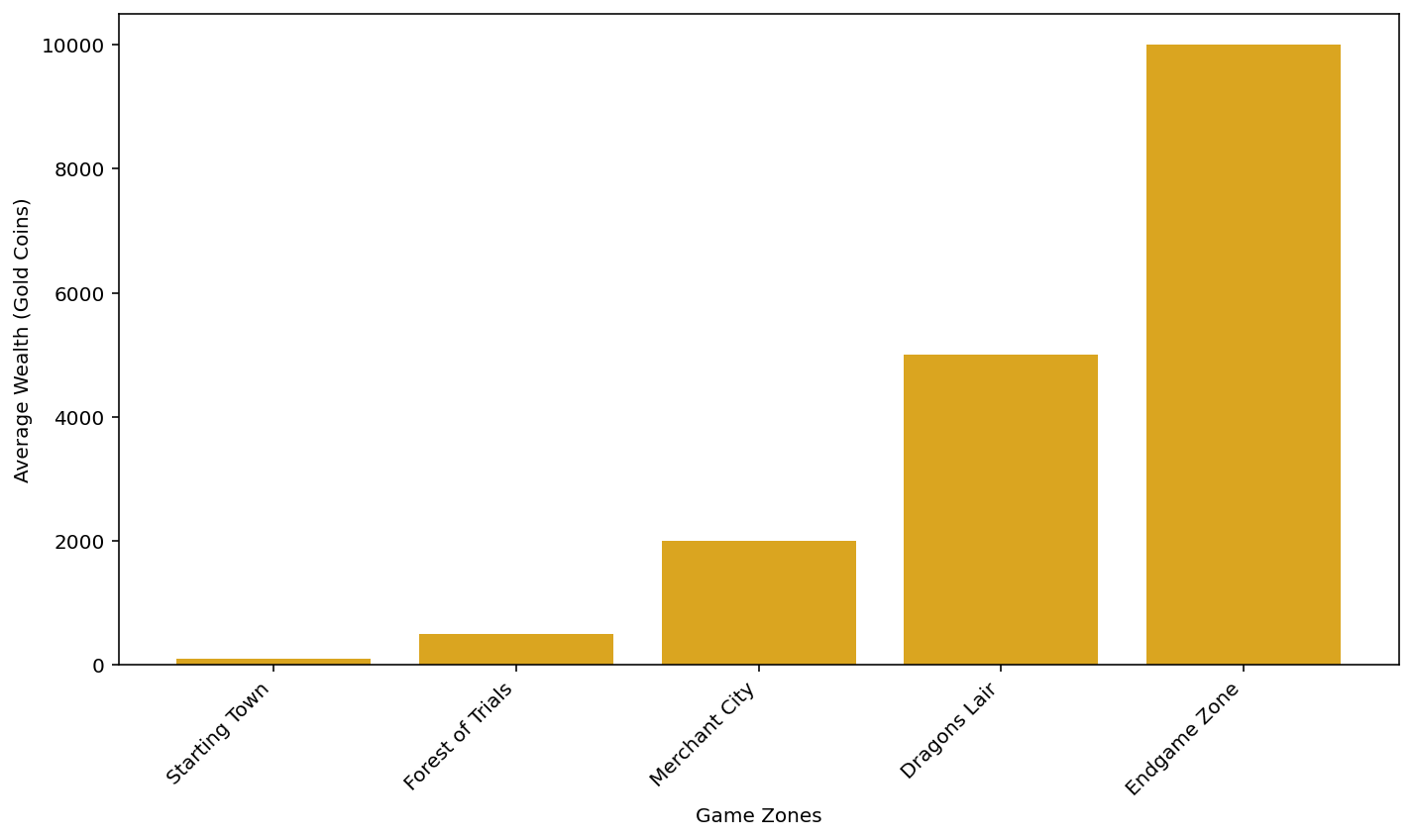
To visualize the economic disparities between different zones in the game world, we’ve compiled data on average player wealth across five major regions. Figure 1 illustrates these differences:

As evident from Figure 1, there is a significant increase in average player wealth as they progress through the game zones. This economic progression serves as a motivator for players to advance in the game, mirroring real-world economic incentives1.
Comparative Analysis of Economic Systems
The diverse economic systems present in “The Good Guys” series offer a rich ground for analysis. Table 1 provides a comparison of these systems:
| Economic System | Primary Currency | Main Economic Activities | Player Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starting Town | Copper Coins | Basic trade, simple quests | Low |
| Merchant City | Gold Coins | Complex trade, investments | High |
| Dragon’s Lair | Dragon Scales | Rare item trade, high-risk ventures | Very High |
As shown in Table 1, the economic systems become more complex and impactful as players progress, offering increasing opportunities for wealth accumulation and economic strategy.
Conclusion
The economic systems in Eric Ugland’s “The Good Guys” series play a crucial role in shaping the game world and driving character progression. From the mathematical model of the in-game economy (Equation 1) to the visual representation of wealth distribution (Figure 1) and the comparative analysis of economic systems (Table 1), we can see how economics is deeply integrated into the series’ narrative and gameplay mechanics.
This analysis demonstrates that Ugland has created a rich, multi-faceted economic environment that not only enhances the realism of the game world but also serves as a key driver of player engagement and story development. As Johnson (2022) notes, such complex economic systems in LitRPG novels contribute significantly to the genre’s appeal and the immersive experience it offers readers.
References
Footnotes
This economic progression system is a common feature in many RPGs and LitRPG novels, serving as a form of “gamified capitalism” that keeps players engaged and motivated.↩︎